Differentiation Formulas List In all the formulas below, f' means \( \frac{d(f(x))}{dx} = f'(x)\) and g' means \(\frac{d(g(x))}{dx}\) = \(g'(x)\) Both f and g are the functions of x and differentiated with respect to x We can also represent dy/dx = D x y Some of the general differentiation formulas are;The derivative of () = for any (nonvanishing) function f is ′ = ′ (()) wherever f is nonzero In Leibniz's notation, this is written (/) =The reciprocal rule can be derived either from the quotient rule, or from the combination of power rule and chain ruleFirst find the differentiation of f′(x0), applying the limit to the quotient If this limit exists, then we can say that the function f(x) is differentiable at x0
Finding The Derivative Using The Limit Definition F X Sqrt X 2 Youtube
How to do (f+g)(x)
How to do (f+g)(x)-Don't try to learn a formula like this You should know the product rule for two functions Well, mathf(x)/math is one function and mathk(x)=g(x)h(x)/math is another So the derivatJan 22, 19 · This is easy enough to prove using the definition of the derivative We'll start with the sum of two functions First plug the sum into the definition of the derivative and rewrite the numerator a little (f(x) g(x))′ = lim h → 0 f(x h) g(x h) − (f(x) g(x)) h = lim h → 0 f(x h) − f(x) g(x h) − g(x) h



Derivatives Pauls Online Math Notes
H(x) = f (x)g (x) h ( x) = f ( x) g ( x) Since f (x)gx f ( x) g x is constant with respect to f f, the derivative of f (x)gx f ( x) g x with respect to f f is 0 0 0 0Oct 08, · In a similar way, the derivative of ln(y) with respect to y is 1/y, the derivative of ln(f(x)) with respect to f(x) is 1/f(x) and the derivative of ln(g(x)) with respect to g(x) is 1/g(x) To find the derivatives of each of the terms with respect to x, we can apply the chain rule by first differentiating with respect to the inner function of lnIn words, this means that the derivative of the substituted function with values \(f(g(x))\), with respect to the variable \(x\) is the product of the derivatives of the constituent functions \(f\) and \(g\), taken at the relevant arguments which are \(x\) itself for \(g\) and \(g(x)\) for \(f\)
A) The function f (g (x)) is the derivative of g in terms of x B) The function f (g (x)) is the product of f (x) and g (x) C) The function f (g (x)) is the result of substituting x in place of the independent variable in the expression for f D) the composition of functions f (g (x)) is the result if substituting g, expressed in terms of theNov 02, · f (g (x)) = tan (2x) ⇒ f' (g (x)) = sec2(2x) = 2sec 2 (2x) Using the chain rule, the derivative of tan (2x) is 2sec2(2x) Finally, just a note on syntax and notation tan (2x) is sometimes written in the forms below (with the derivative as per the calculation above) Just be aware that not all of the forms below are mathematically correct tan2xThe individual derivatives are f'(g) = 3g 2 (by the Power Rule) g'(x) = 5;
These are some steps to find the derivative of a function f(x) at the point x0 doing manual calculations If possible, Simplify the quotient, and cancel Δx;F(x) g(x) thenh0(x)= f0(x)g(x)−f(x)g0(x) g(x)2 • Chain Rule h(x)=f(g(x))thenh0(x)=f0(g(x))g0(x) • Trig Derivatives – f(x)=sin(x)thenf0(x)=cos(x) – f(x)=cos(x)thenf0(x)=−sin(x) – f(x)=tan(x)thenf0(x)=sec2(x) – f(x)=sec(x)thenf0(x)=sec(x)tan(x) – f(x)=cot(x)thenf0(x)=−csc2(x) – f(x)=csc(x)thenf0(x)=−csc(x)cot(x) • Exponential Derivatives – f(x)=ax thenf0(x)=ln(a)ax – f(x)=ex thenf0(x)=ex – f(x)=ag(x) thenf0(x)=ln(a)ag(x)g0(x) – f(x)=eg(x) thenf0(x)=eg(x)g0(xDerivative of x^x, To support my channel, you can visit the following linksTshirt https//teespringcom/derivativesforyouPatreon https//wwwpatreonco




Chain Rule Video Khan Academy




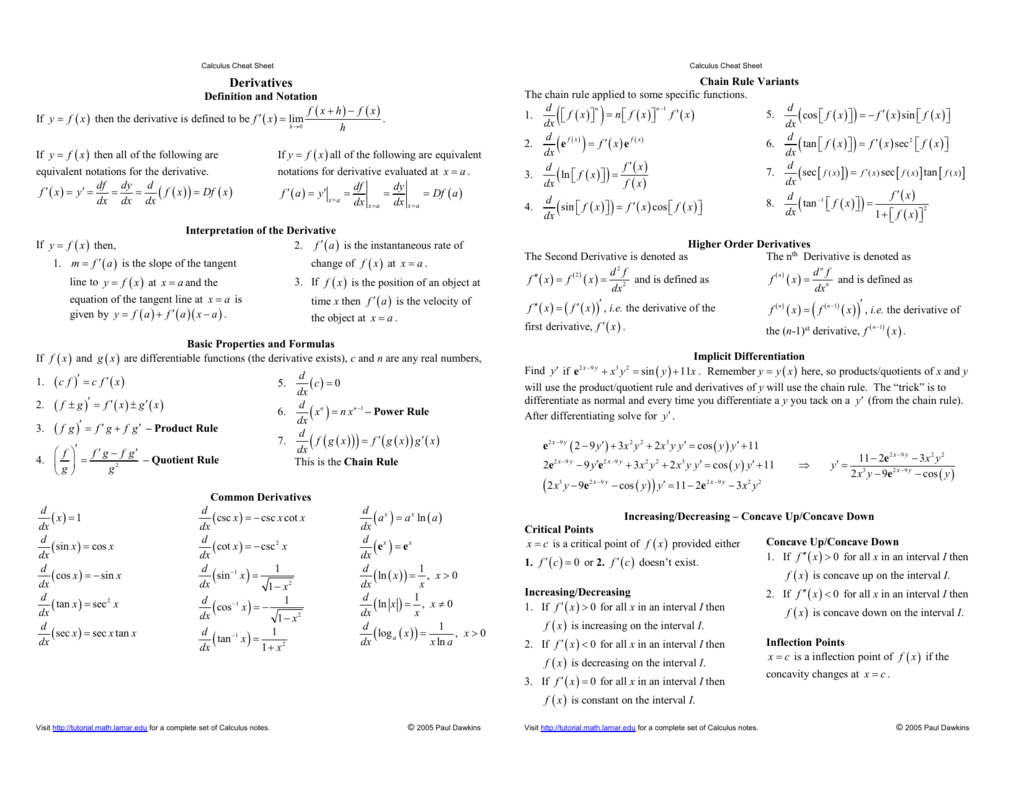
Calculus Cheat Sheet Derivatives
The derivative of f(g(x)) = f'(g(x))g'(x) (5x−2) 3 is made up of g 3 and 5x−2 f(g) = g 3;So ddx (5x−2) 3 = (3g(x) 2)(5) = 15(5x−2) 2The derivative of f(x) at x= ais de ned in terms of a limit f0(a) = lim h!0 f(a h) f(a) h This limit may or may not exist, meaning that the derivative at x= amay or may not exist This leads to Def A function f(x) is di erentiable at x= aif its derivative f0(a) exists That is f(x) is di erentiable at x= a The limit lim h!0 f(a h) f(a) h
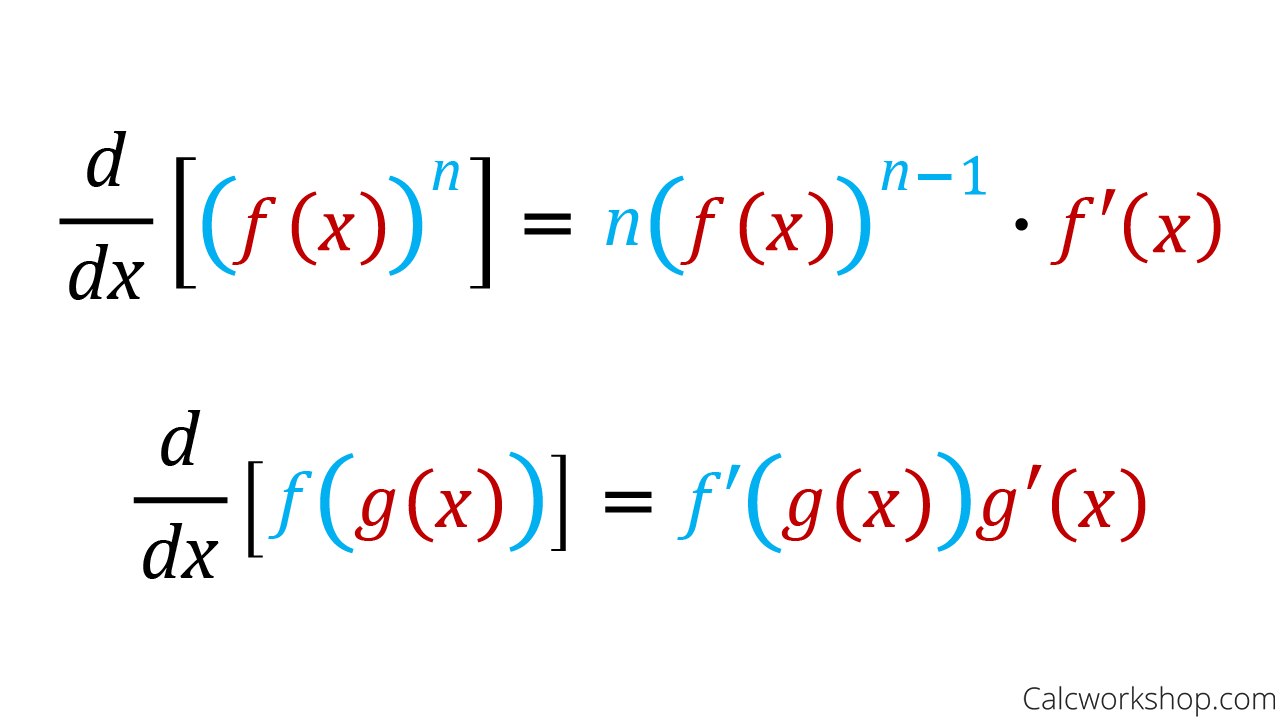



Derivative Rules How To W 7 Step By Step Examples
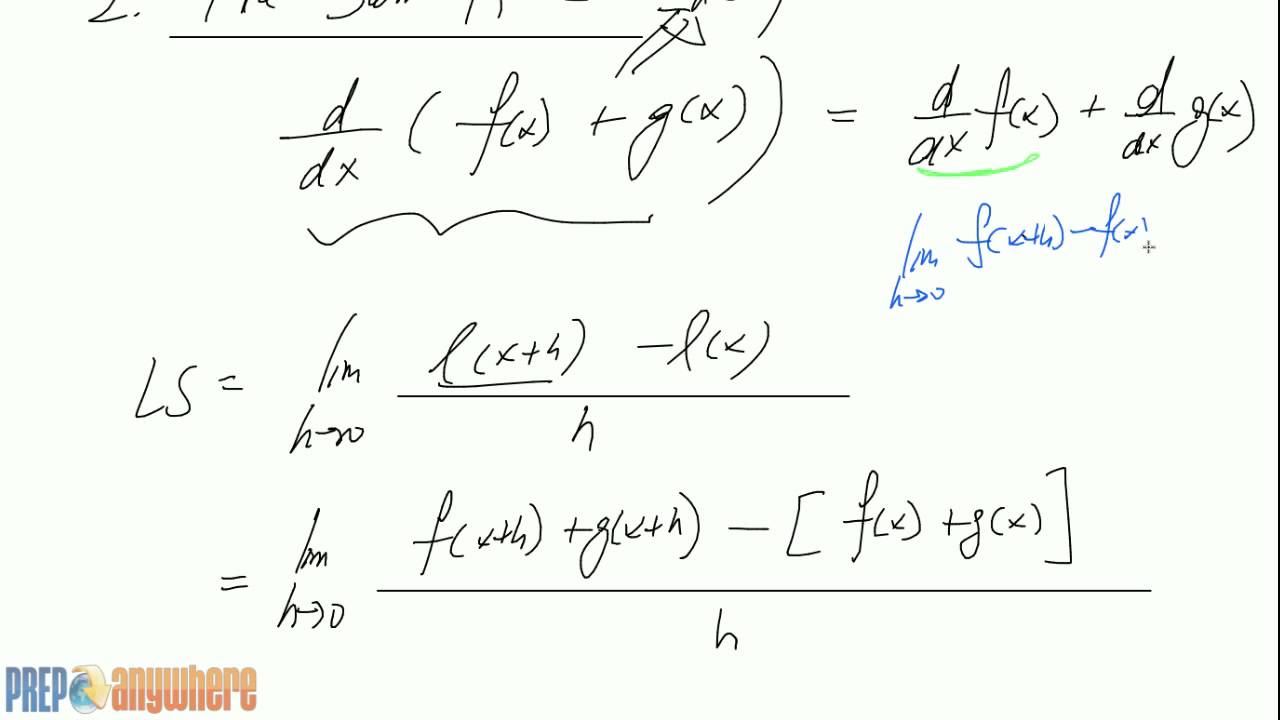



3 Property 2 Derivative Of Sum Of Functions Fx Gx Youtube
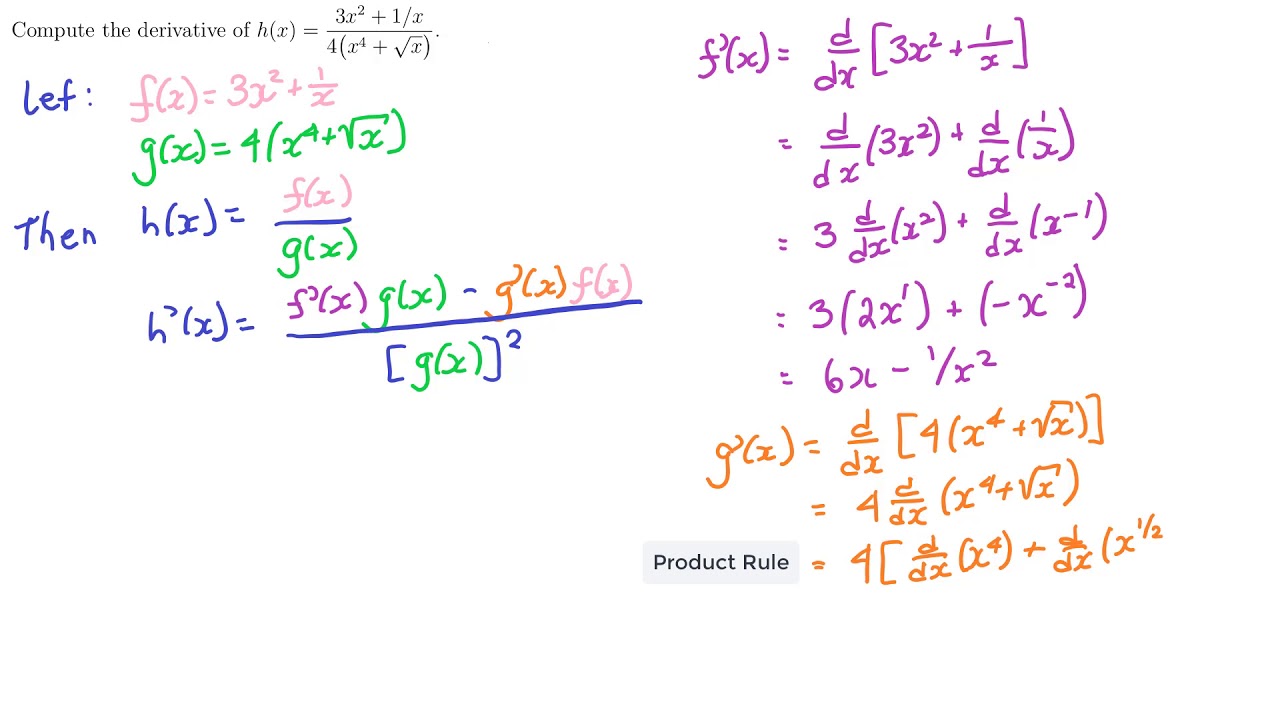
Letting v = g(x h) g(x) h g0(x) we nd g(x h) = g(x) (v g0(x))h with lim h!0 v = 0 Similarly, we can write f(y k) = f(y) (w f0(y))k with lim k!0 w = 0 In particular, letting y = g(x) and k = (v g0(x))h we nd f(g(x)Alternate Proof If f and g are inverse functions and x is in the domain of g, then f ( g ( x )) = x Take the derivative of both sides, using the chain rule on the left f ′ ( g ( x )) g ′ ( x) = 1 Solve for g′ (x) g ′ ( x)If you have function f(x) in the numerator and the function g(x) in the denominator, then the derivative is found using this formula Quotient Rule Derivative formula Take g(x) times the derivative of f(x)In this formula, the d denotes a derivative So, df(x) means the derivative of function f and dg(x) means the derivative of function g
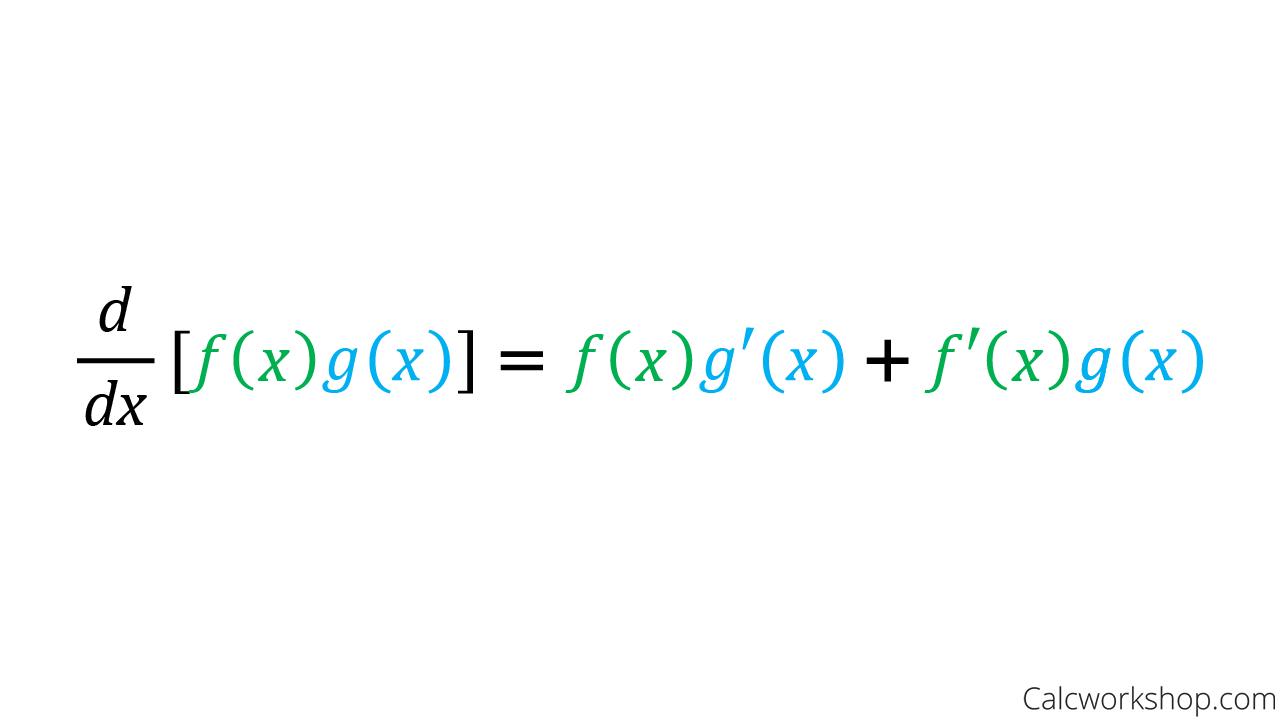



Derivative Rules How To W 7 Step By Step Examples




Econ 213 Elements Of Maths For Economists Ppt Download
Nov 10, · Definition Antiderivative A function F is an antiderivative of the function f if F′ (x) = f(x) for all x in the domain of f Consider the function f(x) = 2x Knowing the power rule of differentiation, we conclude that F(x) = x2 is an antiderivative of f since F′ (x) = 2xGiven f (x) = 3x 2 and g(x) = 4 – 5x, find (f g)(x), (f – g)(x), (f × g)(x), and (f / g)(x) To find the answers, all I have to do is apply the operations (plus, minus, times, and divide) that they tell me to, in the order that they tell me toJan 30, 13 · what I want to do in this video is start with the abstract I guess you could call it formula for the chain rule and then learn to apply it in the concrete setting so let's start off with some function some expression that can be expressed as the product of two functions of two functions so it can be expressed as f of G of X f of G of X so it's a function that can be
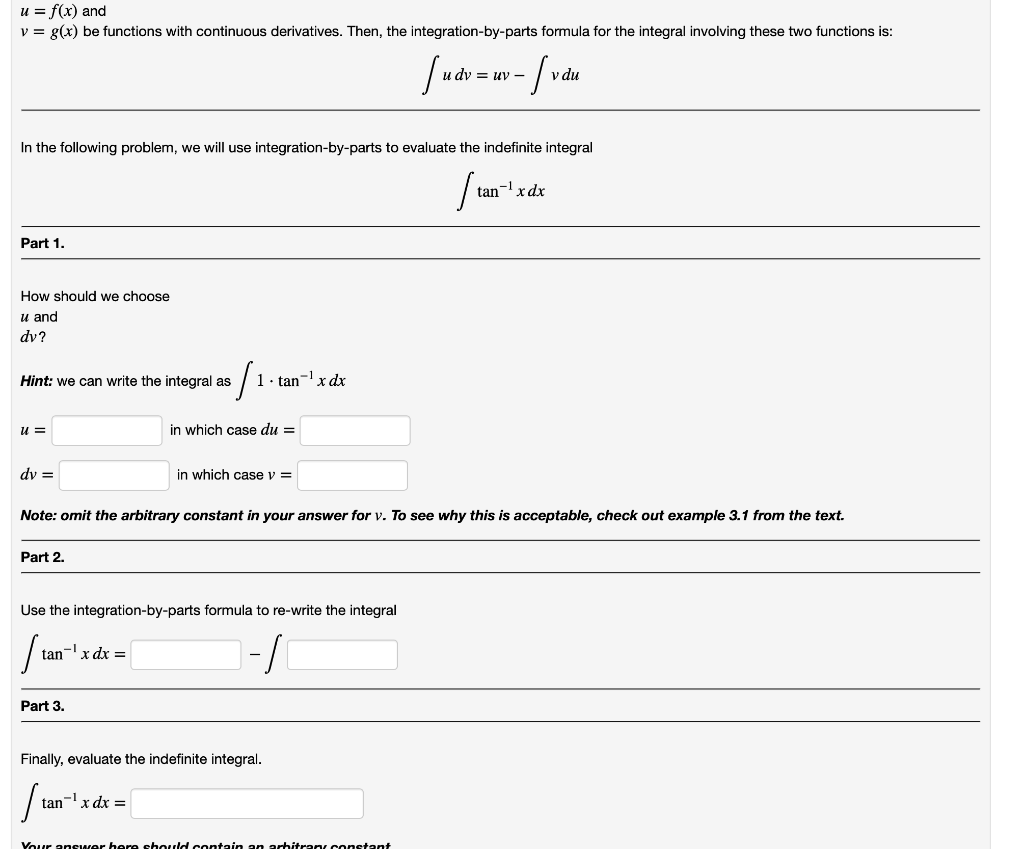



Solved U F X And V G X Be Functions With Continuous D Chegg Com



Finding The Derivative Using The Limit Definition F X Sqrt X 2 Youtube
Jan 16, 19 · Derivative of f(x)^g(x), using logarithmic differentiationShop math tshirts https//teespringcom/stores/blackpenredpenSupport https//wwwpatreoncom/blaDerivatives of the Trigonometric Functions Formulas of the derivatives of trigonometric functions sin (x), cos (x), tan (x), cot (x), sec (x) and csc (x), in calculus, are presented along with several examples involving products, sums and quotients of trigonometric functionsMar 24, 04 · derivative of F (g (x)) wrt x It appears to me that you already did it If you define F (x) and g (x) before the derivative expression, you will get the final result of the chain rule application If you are writing a text book and wish to describe the chain rule, you may have to look elsewhere 0300 AM 0300 AM




First Order Partial Derivatives Of F X Y Ln X 4 Y 4 Youtube



Pdf A Closed Formula For The Derivatives Of Ds E F X
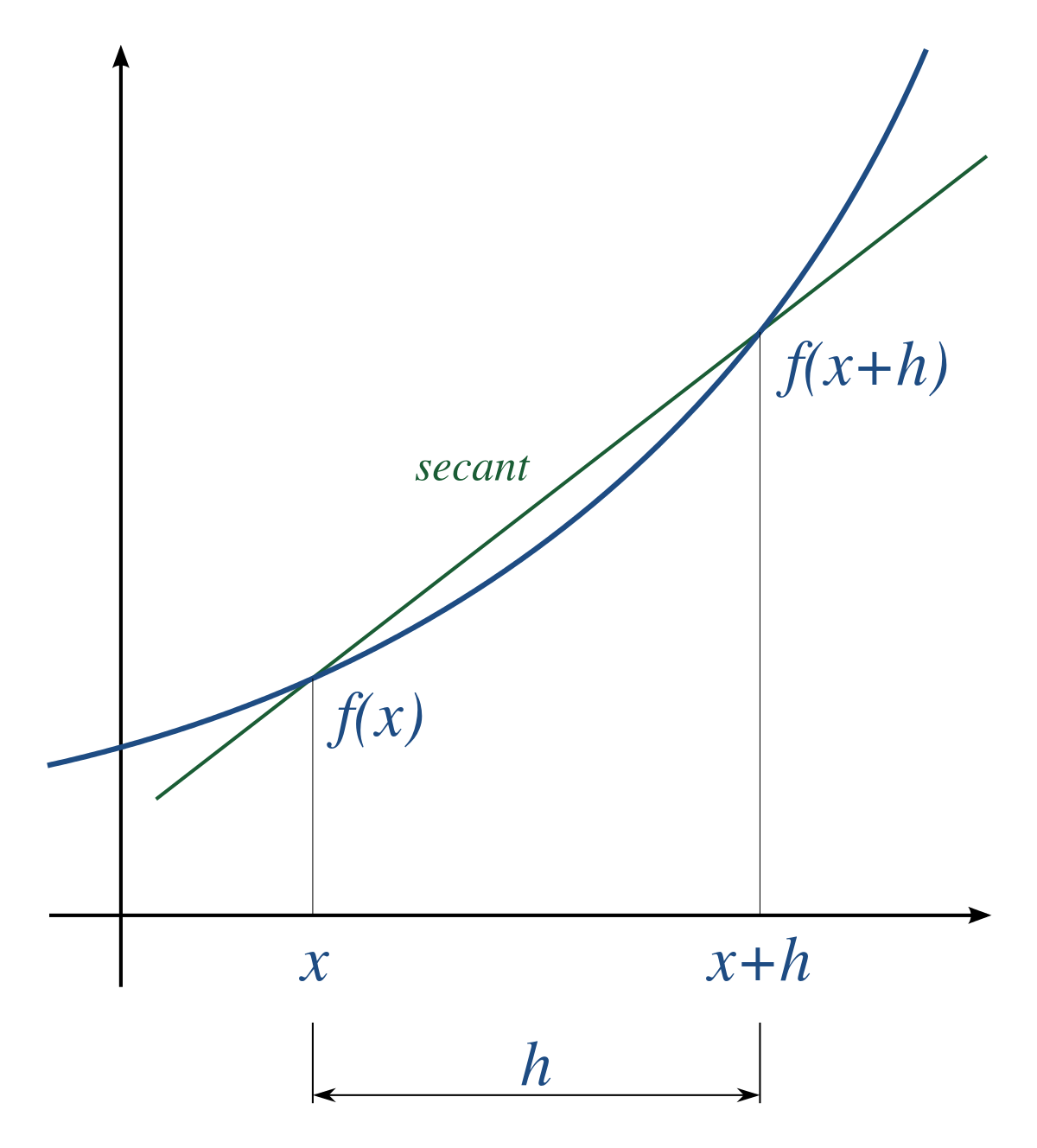
What is the formula for the derivative of f(x) g(x) h(x)?This formula represents the derivative of a function that is sum of functions Example If we have two functions f(x) = x 2 x 1 and g(x) = x 5 7 and y = f(x) g(x) then y' = f'(x) g'(x) => y' = (x 2 x 1)' (x 5 7)' = 2x 1 1 0 5x 4 0 = 5x 4 2x 1 If a function is a multiple of two functions the derivate is given byThe derivative of a function f(x) is written f'(x) and describes the rate of change of f(x) It is equal to slope of the line connecting (x,f(x)) and (xh,f(xh)) as h approaches 0 Evaluating f'(x) at x_0 gives the slope of the line tangent to f(x) at x_0




1 Find The Hundredth Derivative Of P X X 25 Chegg Com




The Derivative Function
Jan 02, 21 · Definition Derivative Function Let f be a function The derivative function, denoted by f ′, is the function whose domain consists of those values of x such that the following limit exists f ′ (x) = lim h → 0f(x h) − f(x) h A function f(x) is said to be differentiable at a if fYou can also get a better visual and understanding of the function by using our graphing tool Chain Rule d d x f (g (x)) = f ' (g (x)) g ' (x) Step 2 Click the blue arrow to submit Choose "Find the Derivative" from the topic selector and click to see the result!Step 1 Choose f (x) and g (x) The denominator (bottom function) is g (x) x 5 Step 2 Find f′ (x) and g′ (x) (the derivatives of f and g) Step 3 Plug your functions (from Step 1) and their derivatives (Step 2) into the quotient rule formula More examples for the Quotient Rule



The Derivative Of Sum Of Functions Formula And Example Lunlun Com




Chapter 3 Study Guide Trigonometric Functions Derivative
In this chapter we investigate how the limit definition of the derivative leads to interesting patterns and rules that enable us to quickly find a formula for \(f'(x)\) without directly using the limit definition For example, we would like to apply shortcuts to differentiate a function such as \(g(x) = 4x^7 \sin(x) 3e^x\text{}\)We can then apply the chain rule to find (g(f(x)))' = 0' = 0 = g'(f) * f '(x), and this equation will determine f ' in terms of f This is actually the general idea used above to evaluate the derivatives both of and h 1 (the reciprocal and the inverse functions to h)Dec 16, 14 · It's f^prime(g(h(x))) g^prime (h(x)) h^prime(x) Start by defining the function a(x)=g(h(x)) The the chain rule gives us (f @ g @ h)^prime (x)=(f @ alpha)^prime (x)=f^prime(alpha(x)) alpha^prime(x) Applying the definition of alpha(x) to the equation above gives us f^prime(alpha(x)) alpha^prime(x) = f^prime (g(h(x))) (g @h)^prime (x) Using the chain rule again f^prime (g(h(x))) (g




Derivatives Pauls Online Math Notes
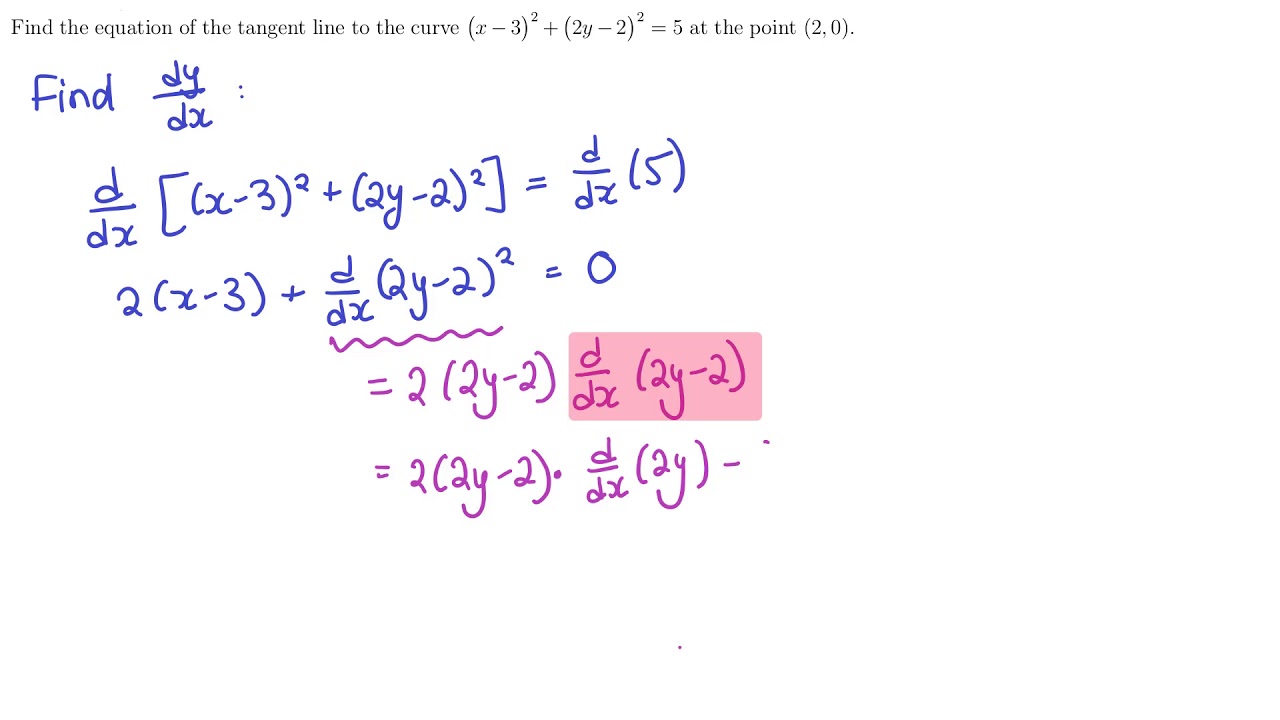



Implicit And Logarithmic Differentiation
Product rule The product rule is a formula that is used to determine the derivative of a product of functions There are a few different ways that the product rule can be represented Below is one of them Given the product of two functions, f (x)g (x), the derivative of the product of those two functions can be denoted as (f (x)·g (x))'If f(x) and g(x) are differentiable functions, then the derivative of the product fg with respect to x is given by (fg)' = f 'g f g' This can be fairly easily derived from the definitionThe derivative of the logarithmic function {eq}\ln(f(x)) {/eq} is equivalent to the ratio of the derivative of {eq}f(x) {/eq} and {eq}f(x) {/eq} Writing this as a formula generates
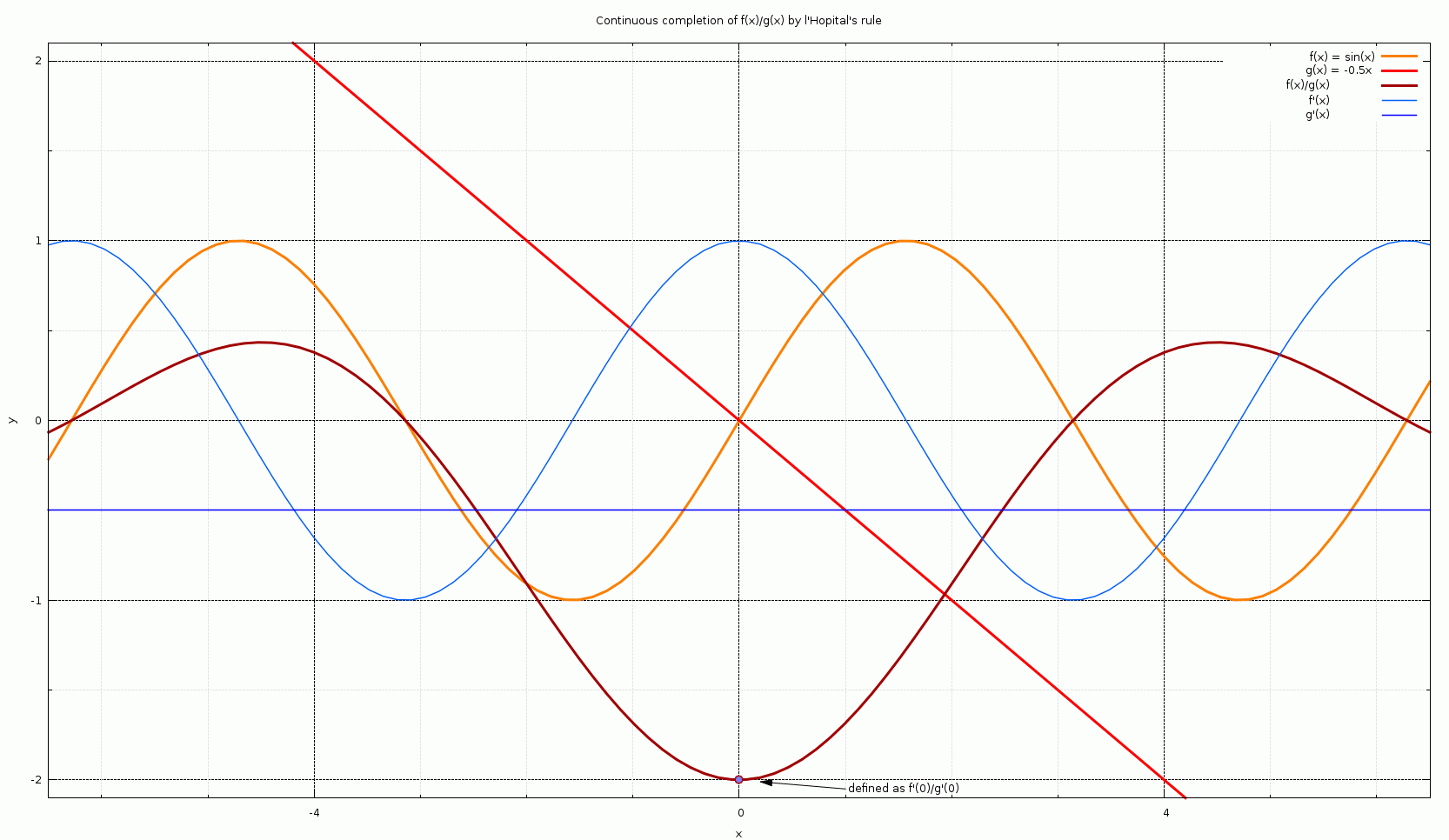



L Hopital S Rule Wikipedia
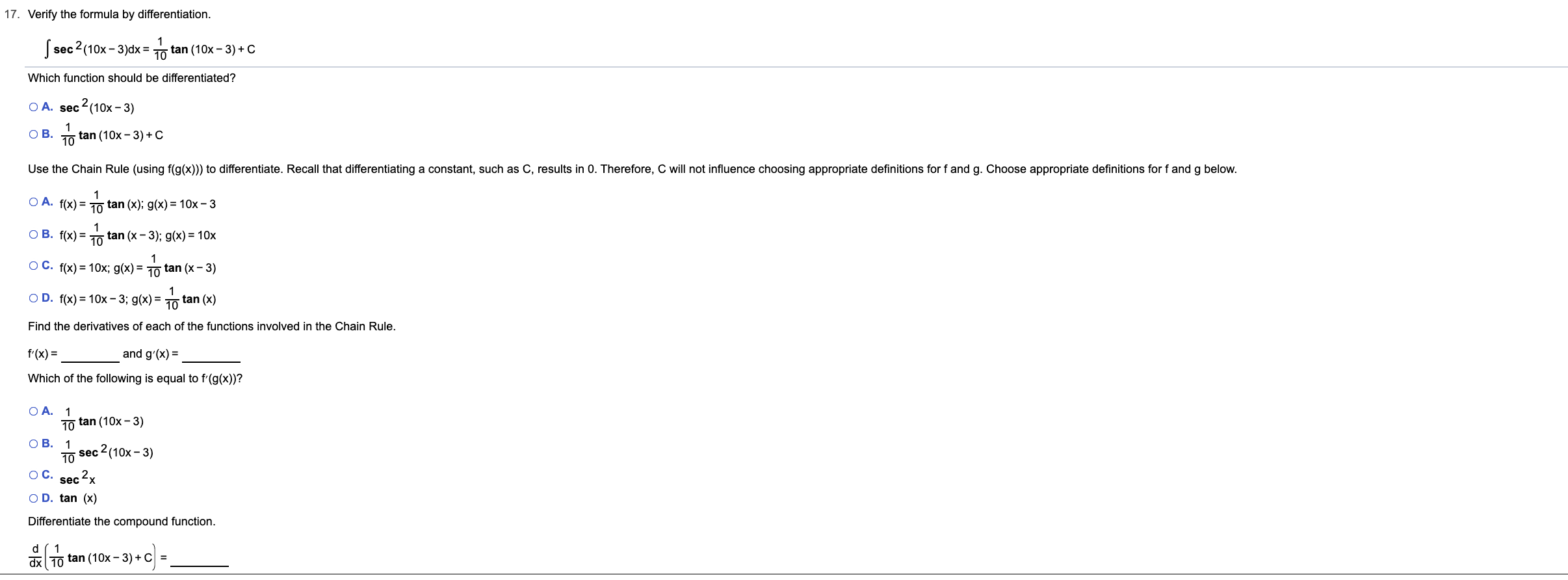



Answered 17 Verify The Formula By Bartleby
Aug 18, 18 · Basic Derivative formula ( c) = 0, where c is constant ( x) = 1 ( xn) = n x n1 f (x) n = n f (x) n1 f (x) C∙f (x) = C ∙ f (x) = C ∙ f' (x) f (x) ∙ g (x) = f (x) g (x) g (x) f (x) This is called product rule of derivative This is quotient rule of derivativeIn doing this, the Derivative Calculator has to respect the order of operations A specialty in mathematical expressions is that the multiplication sign can be left out sometimes, for example we write "5x" instead of "5*x" The Derivative Calculator has to detect these cases and insert the multiplication sign\frac{d}{dx}(\frac{3x9}{2x}) \frac{d^2}{dx^2}(\frac{3x9}{2x}) (\sin^2(\theta))'' derivative\of\f(x)=34x^2,\\x=5;




Chapter 8 Differential Calculus Pdf Free Download
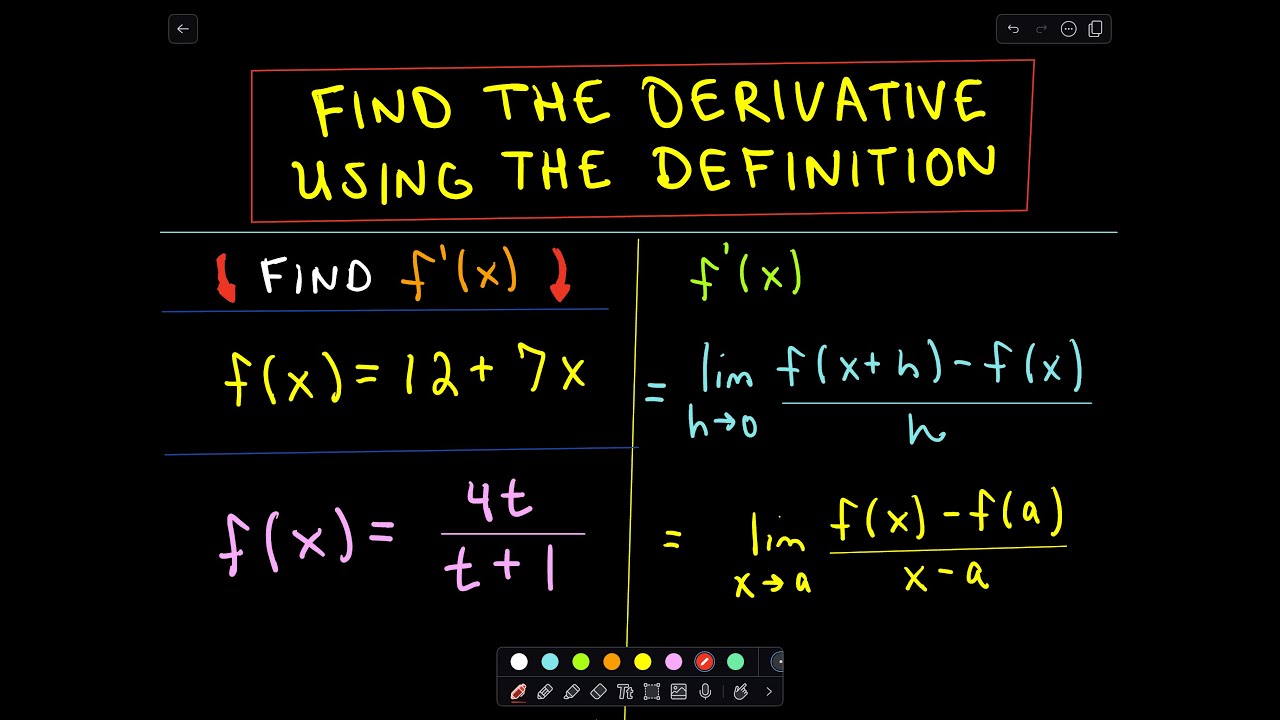



Finding A Derivative Using The Definition Of A Derivative Youtube
If g is the inverse of f, the derivative of f (x) is 1/g' (f (x)), not 1/f' (x) In this case, g' (x)=e^x, so the derivative of ln (x) is 1/ e^ (ln (x))=1/x (1 vote)$\log (h(x))=g(x) \log (f(x))$ $\frac{h'(x)}{h(x)}=g'(x) \log (f(x))\frac{g(x)f'(x)}{f(x)}$ Thus, $h'(x)=h(x)\left(g'(x) \log (f(x))\frac{g(x)f'(x)}{f(x)}\right)$Implicit\derivative\\frac{dy}{dx},\(xy)^2=xy1 \frac{\partial}{\partial y\partial x}(\sin (x^2y^2)) \frac{\partial }{\partial x}(\sin (x^2y^2))
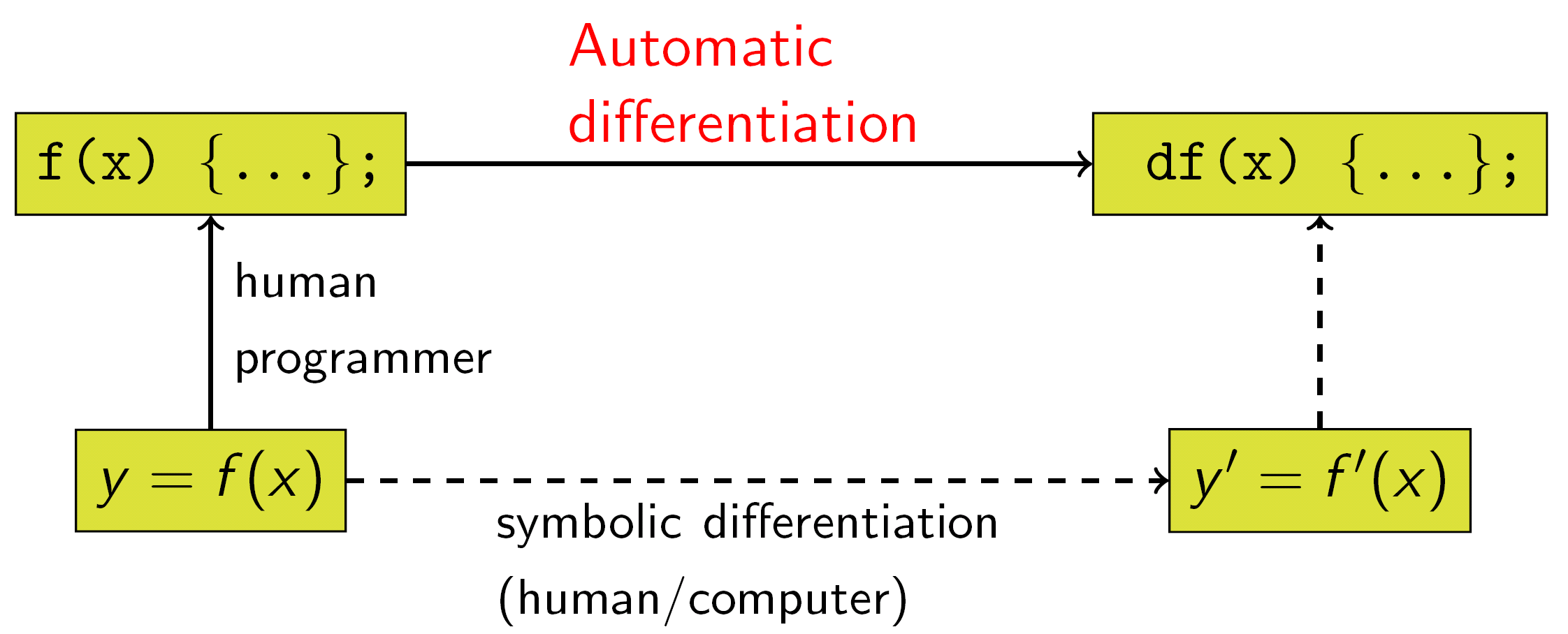



Automatic Differentiation Wikipedia




The Derivative Of Sec 2x Derivativeit
Power Rule (d/dx) (x n ) = nx n1Suppose h ( x) = f ( x) g ( x), where f and g are differentiable functions and g ( x) ≠ 0 for all x in the domain of f Then The derivative of h ( x) is given by g ( x) f ′ ( x) − f ( x) g ′ ( x) ( g ( x)) 2 "The top times the derivative of the bottom minus the bottom times the derivative of the top, all over the bottom squaredThe derivative of f(x) evaluated at g(x) times the derivative of g(x) Proof By the de nition of the derivative we have d dx f(g(x)) = lim h!0 f(g(x h)) f(g(x)) h Since g is di erentiable at x;




Solved 1 D A Find Cosº X Dx B Let F G R R Be Chegg Com




Derivative Formulas The Definition Of The Derivative
Transcribed image text Find the derivative of the function g(x) et 4 33 5 22 3 x2 find f'(x) = If f(a) 4x2 8x 3 Vä then f'(a) = f(1) = Previous question Next question Get more help from Chegg Solve it with our calculus problem solver and calculator COMPANY About Chegg;Dec 01, · The derivative of f (x) is mostly denoted by f' (x) or df/dx, and it is defined as follows f' (x) = lim (f (xh) f (x))/h With the limit being the limit for h goes to 0 Finding the derivative of a function is called differentiation Basically, what you do is calculate the slope of the line that goes through f at the points x and xhCf(x) = c d f(x) = cf′(x), and (f(x)g(x))′ = d dx (f(x) g(x)) = d dx f(x) d dx g(x) = f′(x) g′(x) It is easy to see, or at least to believe, that these are true by thinking of the distance/speed interpretation of derivatives If one object is at position f(t) at time t, we know its speed is given by f′(t) Suppose another object




How Do You Differentiate G Y 60x 2 74 E 3 X Using The Product Rule Socratic




Remarkably The Chain Rule Allows You To Calculate Chegg Com
Added Aug 1, 10 by ihsankhairir in Mathematics To obtain the composite function fg(x) from known functions f(x) and g(x) Use the hatch symbol # as the variable when inputting




Quotient Rule Derivatives Video Khan Academy




Mathematics Basic Elementary Function Derivative Formula And Derivation Rules Programmer Sought
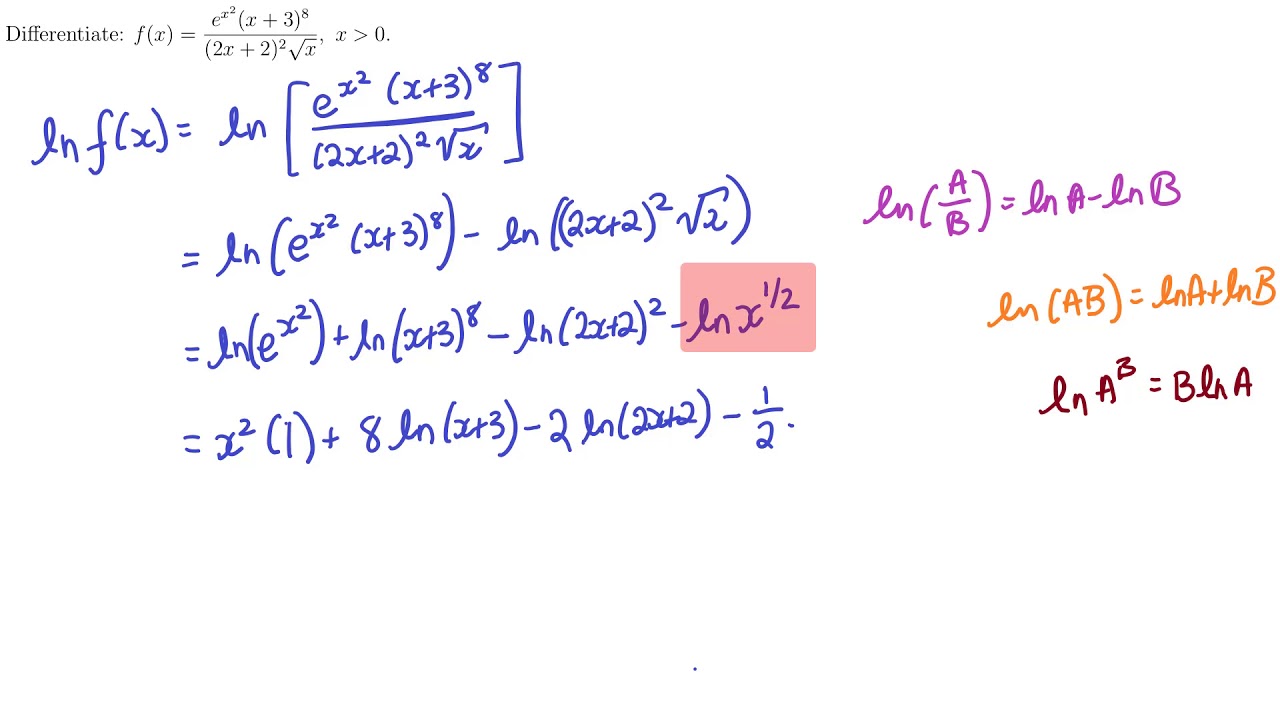



Implicit And Logarithmic Differentiation




Limits And Derivatives Formulas Derivative Mathematical Relations
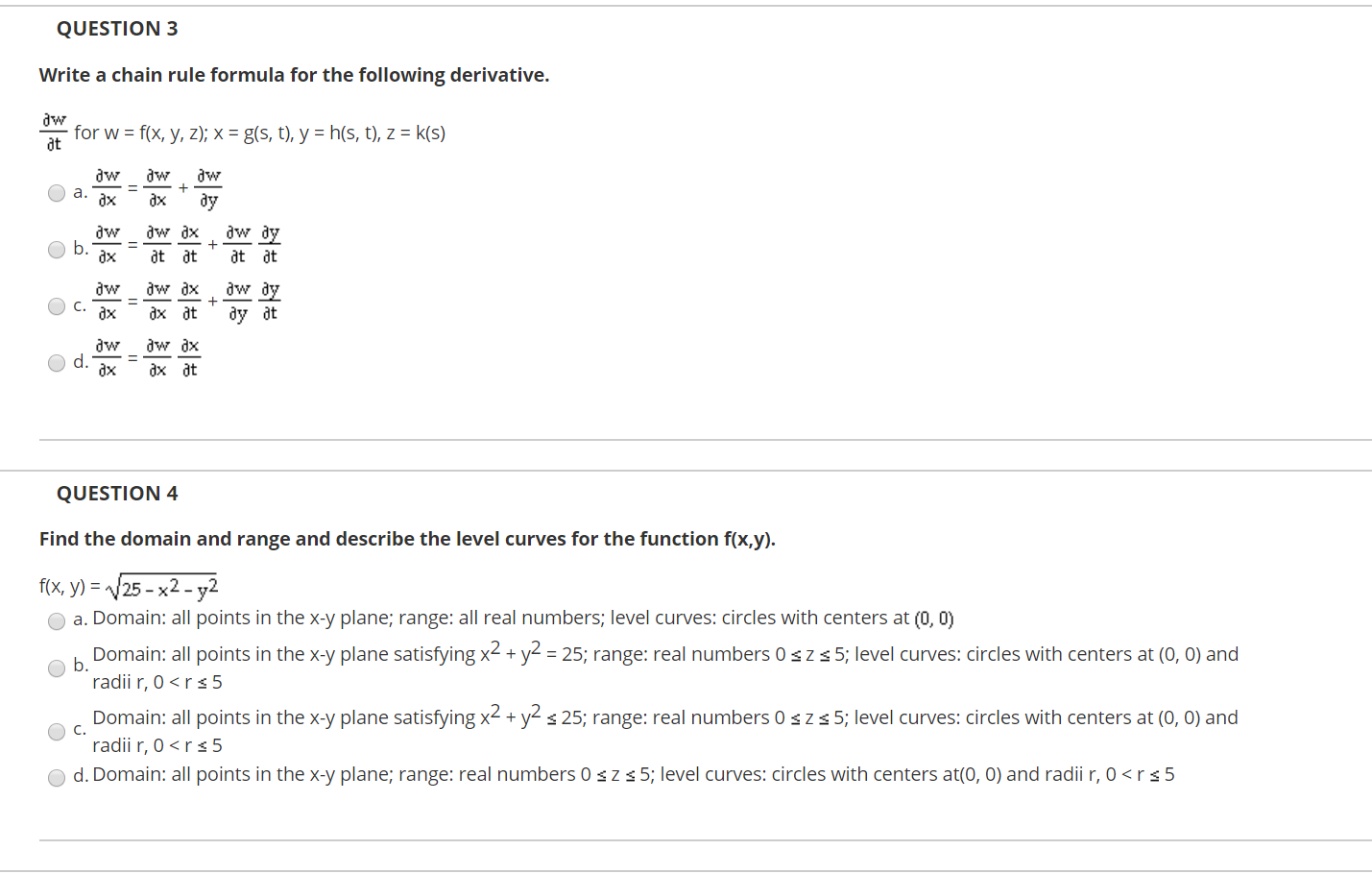



Question 3 Write A Chain Rule Formula For The Chegg Com




Differentiation Formula By Tutorcircle Team Issuu
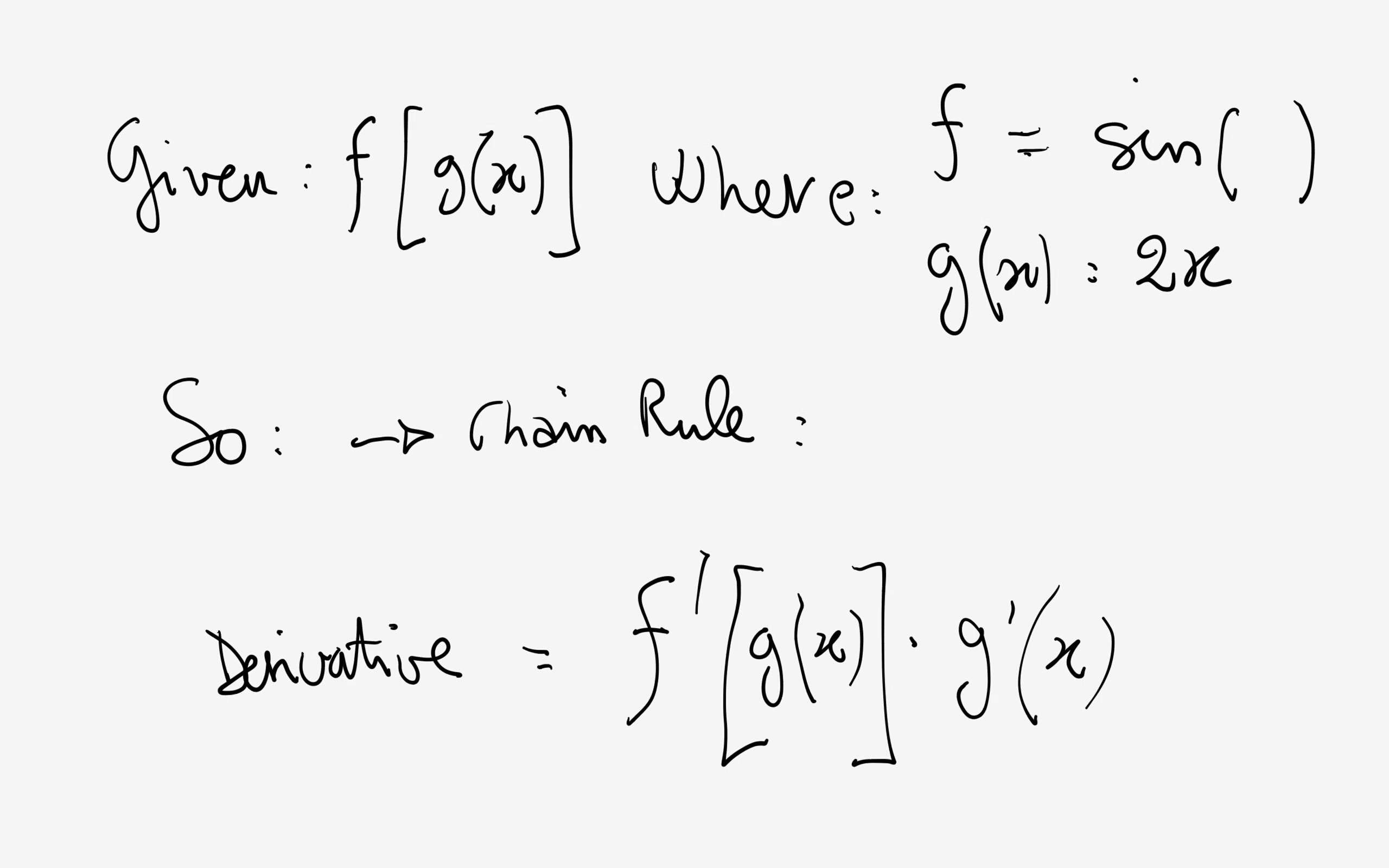



What Is The Derivative Of Sin 2x Socratic




If F X 2 X 2 3 X And G X 2e X 4 How Do You Differentiate F G X Using The Chain Rule Socratic



Numerical Differentiation Wikipedia




How To Make Calculus Easier A Fast Way To Find The Derivative Of A Function Owlcation




The Derivative



Finding The Derivative Of F X X 2 X 3 By Using The Definition Youtube




Answered A Three Times Differentiable Function Bartleby




Derivatives Of Inverse Functions Video Khan Academy



Derivative Rules




18 Calculus Teacher Ideas Calculus Teacher Calculus Studying Math




Ex 13 2 9 Find Derivative Of I 2x 3 4 Ii 5x 3 3x 1 X 1




The Chain Rule Theorem Chain Rule Ppt Download



Calculus Index Cards



Worked Example Chain Rule With Table Video Khan Academy
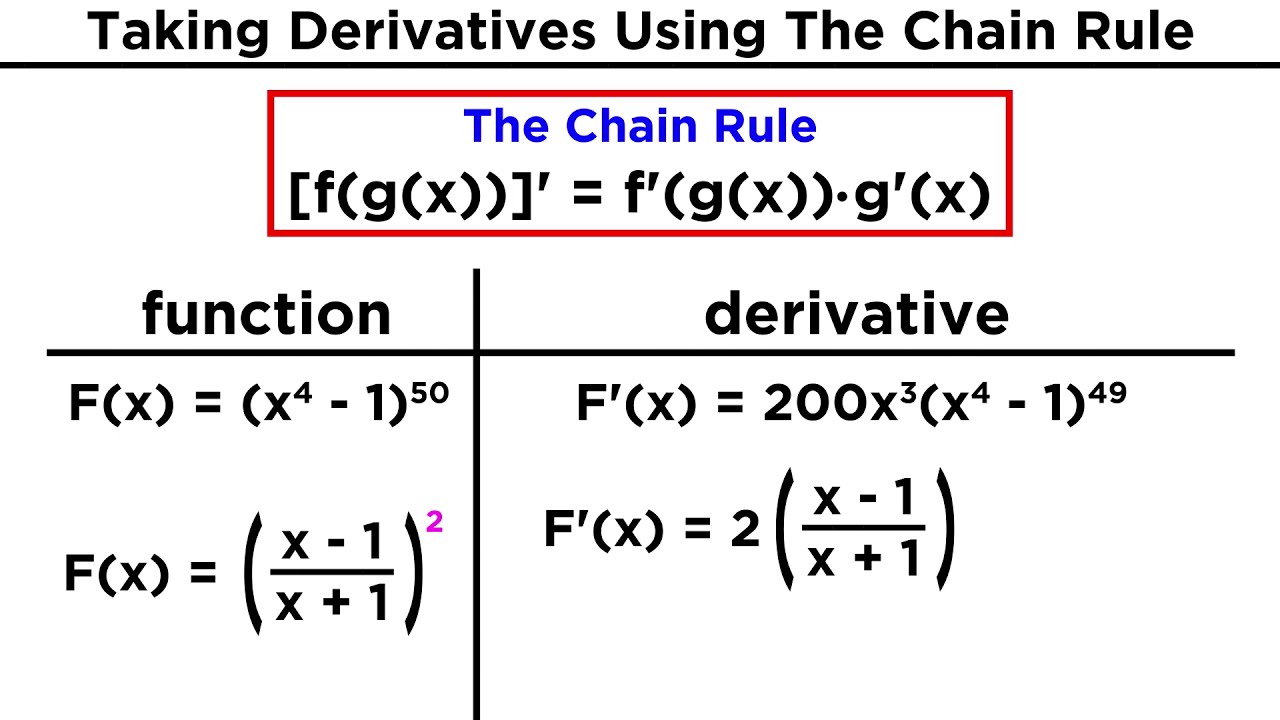



Derivatives Of Composite Functions The Chain Rule Youtube



Second Derivative Quotient Rule Purgweb
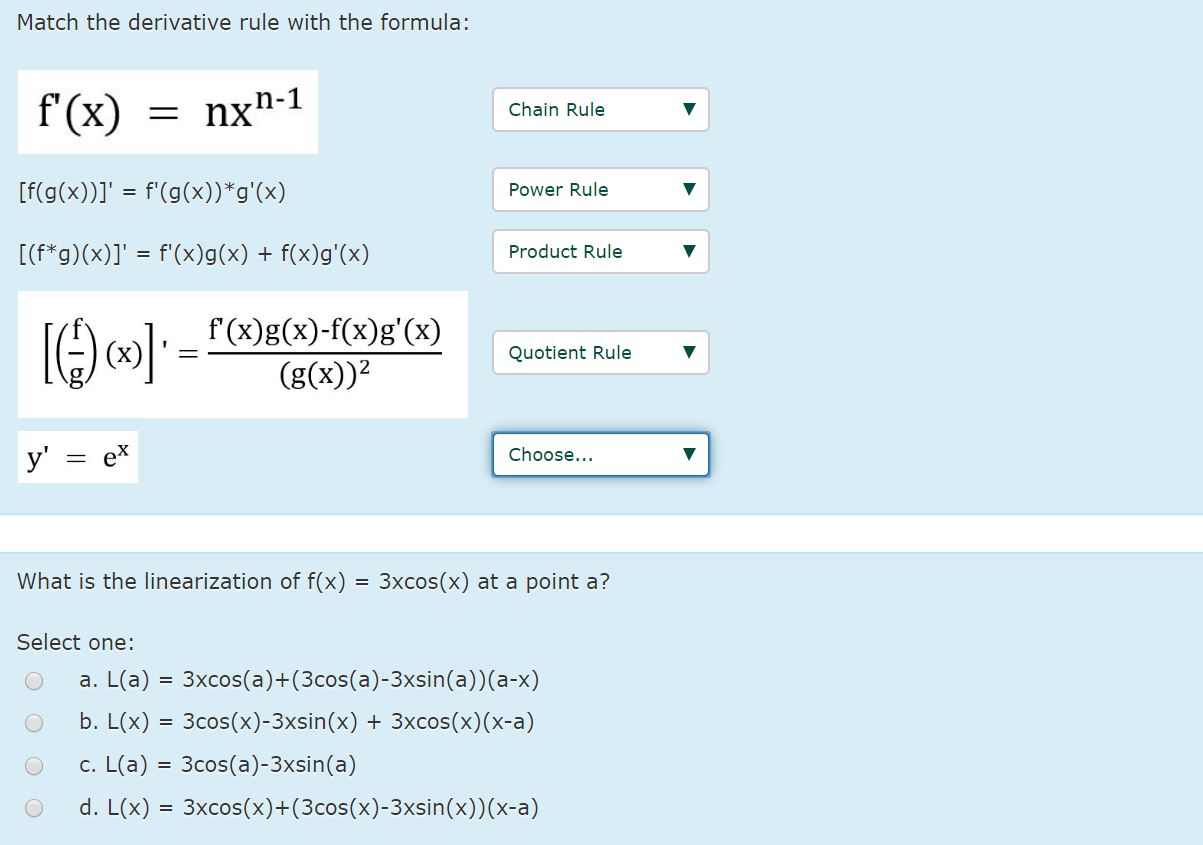



Match The Derivative Rule With The Formula F X Chegg Com




4 1 Simple Derivative Rules And Applications Function




How To Prove Eulers Formula Using The Definition Of Derivative Mathematics Stack Exchange




Formula Sheet Trigonometric Functions Sine




Lesson 59 Derivatives Of Composed Functions The Chain Rule Ppt Download




Partial Derivative Examples Math Insight




Finding Derivative With Fundamental Theorem Of Calculus Video Khan Academy




The Product Rule Gives The Formula D Dx F X G X Chegg Com




Calculus I Derivative Using Definition F X 3x 2 5x Youtube




Ex 13 2 4 Find Derivative From First Principle I X3 27




Preparing Precalculus Preparing Precalculus Sheet Help In Academic Math




A Find The Stationary Points Of F X 2x2 3x Chegg Com




Answered Use The Table To The Right To Find The Bartleby




Formulas For Exam Studocu
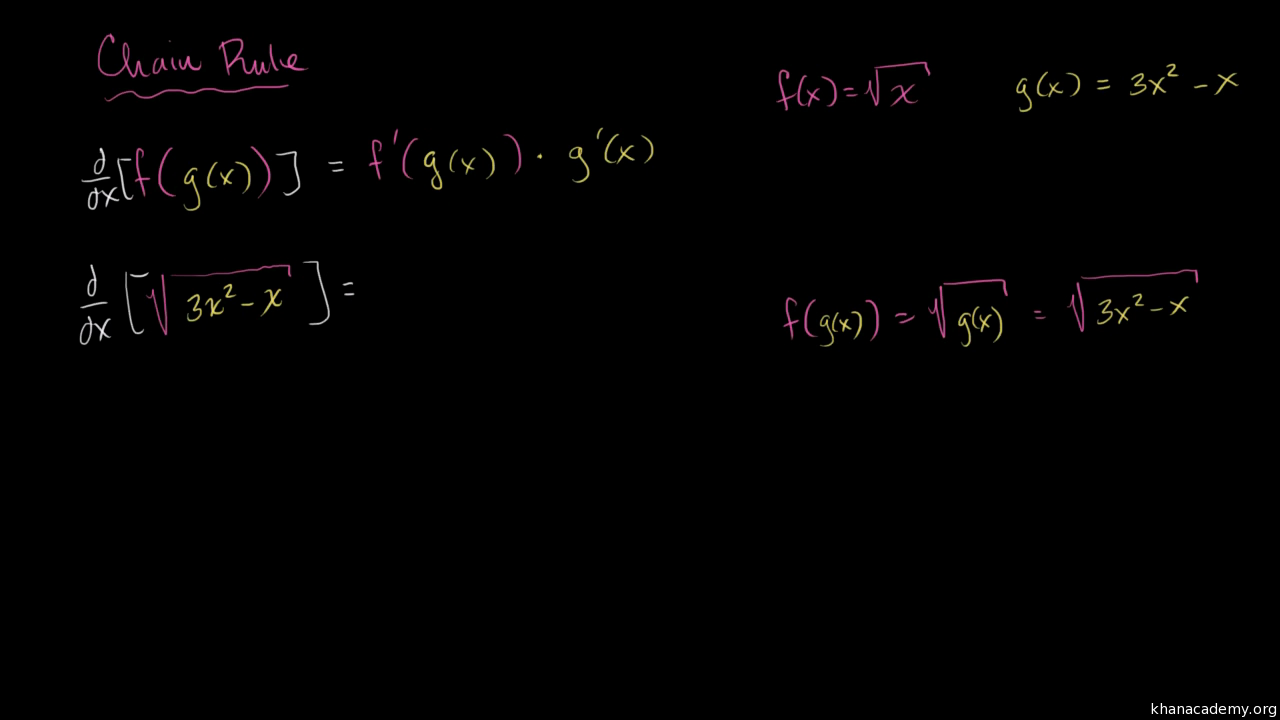



Worked Example Derivative Of 3x X Using The Chain Rule Video Khan Academy




Manipulating Functions Before Differentiation Video Khan Academy




Calculus Cheat Sheet Derivatives Maxima And Minima Derivative
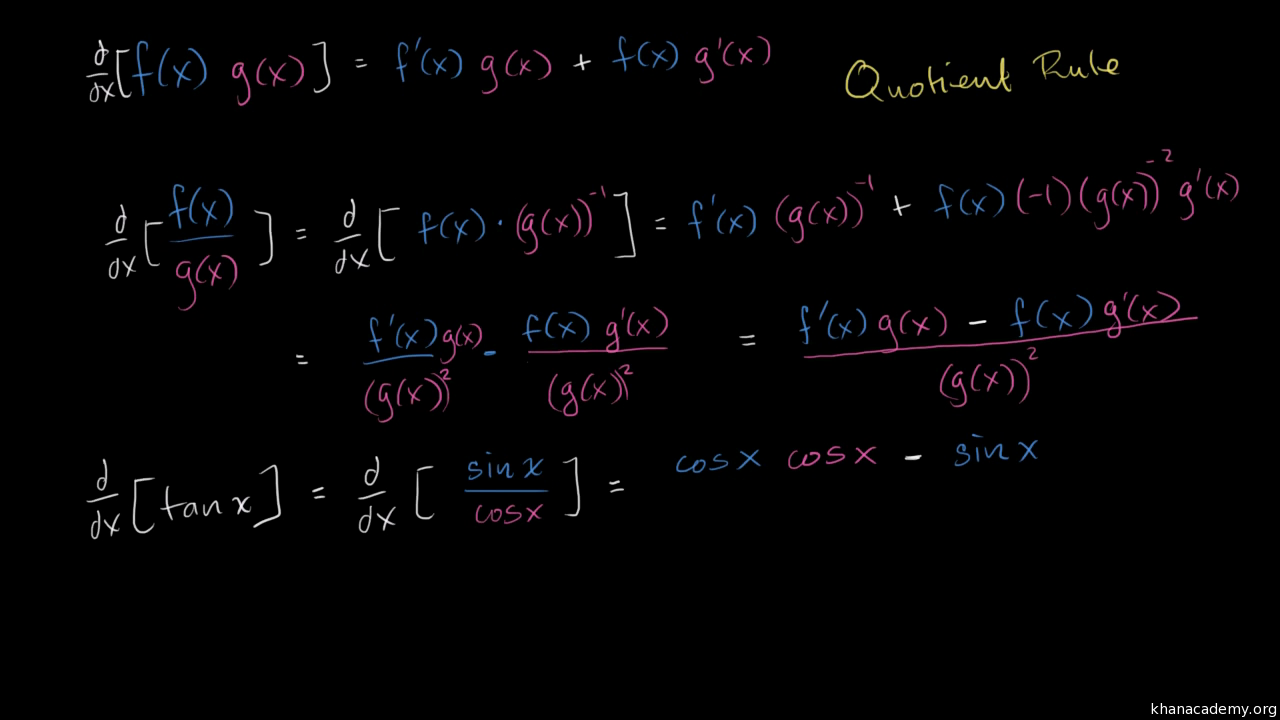



Derivative Of Tan X Old Video Khan Academy




The Manga Guide To Calculus Amazon It Kojima Hiroyuki Togami Shin Libri In Altre Lingue




Applications Of The Derivative Ppt Download
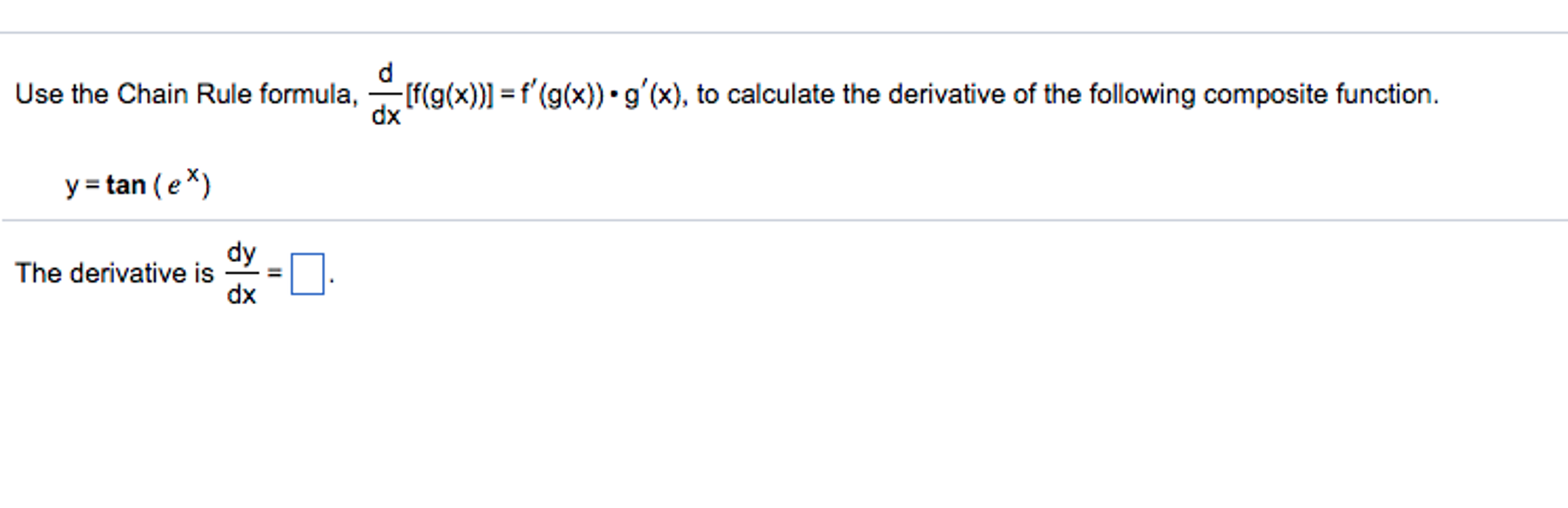



Solved Use The Chain Rule Formula D Dx F G X F G X Chegg Com




Derivative Of Aˣ For Any Positive Base A Video Khan Academy




The Chain Rule Theorem Chain Rule Ppt Download




1 Consider The Equation Y F X G X Find Dy By Chegg Com




Higher Derivatives Section 3 8



Basic Derivative Rules Table Video Khan Academy




Calculus Cheat Sheet Derivatives Reduced Copy




The Quotient Rule Derivativeit




Derivatives Of Inverse Functions From Equation Video Khan Academy




How To Find Derivative Using Formula Definition Of The First Derivative Youtube



Derivatives Of Exponential Functions Youtube



Applications Of The Derivative Ppt Download




Inverse Of Derivatives




Answered D Y 0 140 If Y X 1 X 2 X Bartleby




Formula Class 12 Application Of Derivatives




Calculus Cheat Sheet Derivatives Studocu
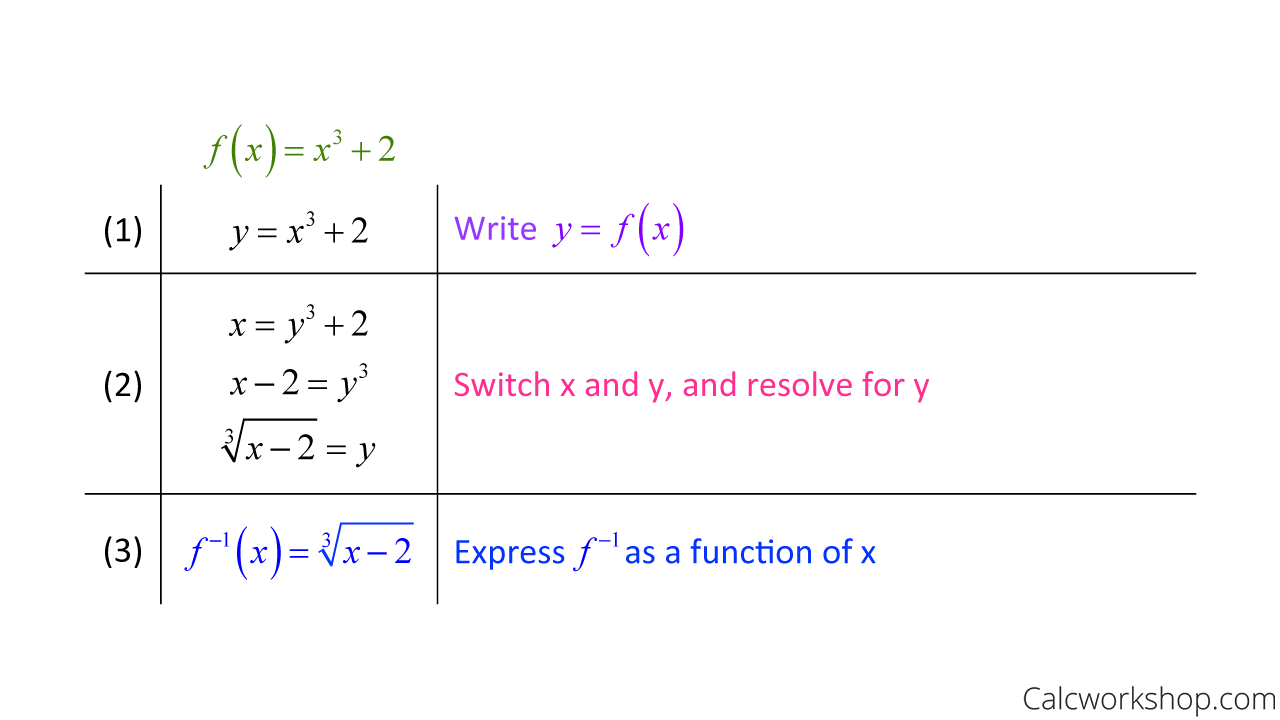



Derivative Of Inverse Functions How To W Examples



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿